The Delilah missile is a cruise missile or loitering munition developed in Israel by Israel Military Industries (now Elbit Systems Land). It is designed to target moving and re-locatable targets with a circular error probable (CEP) of 1 metre (3 ft 3 in). Unlike a typical cruise missile, which is locked onto a pre-programmed target prior to launch, the Delilah missile’s unique feature, as claimed by the manufacturer, is being able to loiter and surveil an area before a remote weapon systems officer, usually from the launching fighter aircraft, identifies the specific target of the attack. The Delilah missile was first used in combat by Israel over Lebanon in July and August 2006 and launched by F-16D fighter aircraft. On 9 May 2018, Delilah missiles were fired at Syrian and Iranian targets, including anti-aircraft systems, such SA-5, SA-2, SA-22, and SA-17 units.
The name Delilah had been used by an anti-radiation attack drone configured after the US MQM-74 Chukar aerial target. It entered service in the Israeli Air Force in the mid-1980s. This air-launched drone identifies radar sites, allowing them to be found and destroyed. The Delilah missile is the name of a missile family built by IMI. Delilah was initially created as an aerial decoy, and was later developed into an offensive strike weapon in the 1990s, used by Israeli F-16 and upgraded F-4E attack aircraft. It is multi-platform and has multi-target capability. Its uses include Air-to-Surface (AS) and Surface-to-Surface (SS), targeting ground targets, vehicles and sea vessels, either stationary or moving. It is classed as a Medium Range, Multi-Purpose Guided Missile (MRMPGM), as All-in-One. It was Combat-Proven in Lebanon by Israeli Forces.

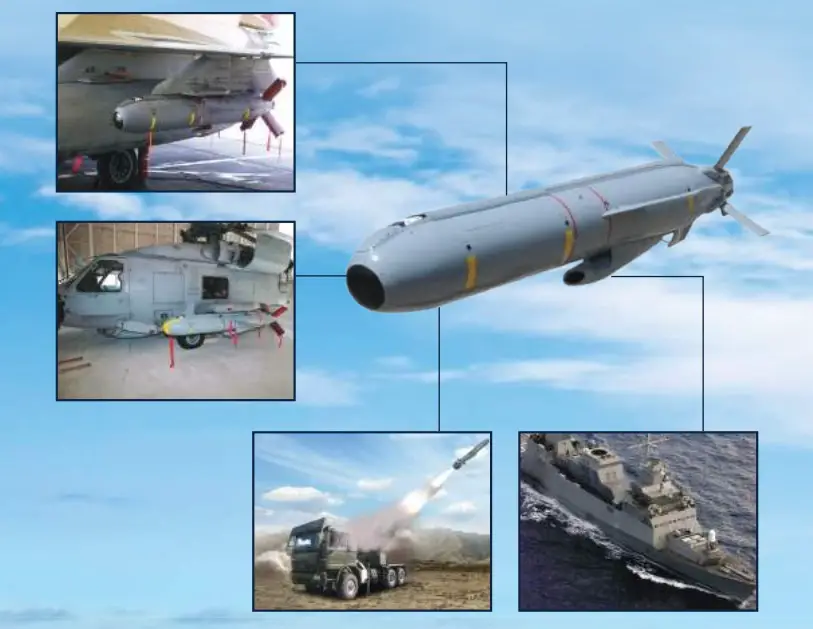
The Delilah is an air-launched stand-off missile and cruise missile with a range of 250 km. It can be fitted with a variety of warheads which can be targeted on both land and sea targets. It has a turbo jet engine that is able to loiter, allowing it to target well-hidden threats in addition to moving targets. Its maneuverability makes the missile ideal for destroying surface-to-air missile threats. The on-board autopilot and inertial navigation-global positioning navigation systems (INS/GPS) allow the missile to perform its mission autonomously. A data link enables intervention and target validation. The missile can be fired from most aircraft, helicopters, or ground launchers. Its compact dimensions allow it to be carried by the Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk and SH-60B helicopters.
The Delilah missiles deliver pinpoint accuracy for precision deep strikes and surgical hits against moving, stationary or re-locatable targets. The missile features an advanced electro-optical (E/O) seeker for day/night and all weather target discrimination, a cruise speed of Mach 0.5 to 0.7 and a maximum range of 250 km. Delilah offer a preprogrammed mission with post-launch updates, and Man-in-the-Loop override capability for target selection and final attack approval that enables real-time, in-flight target-of-opportunity designation for target acquisition and attack (re-attack), and battle damage assessment (BDA).Delilah is a combat proven and operational missile for various fixed-wing aircraft, with helicopter, ground and ship-launched versions Delilah HL, Delilah GL and Delilah SL. The missiles are operable on land, in littoral waters and open sea.